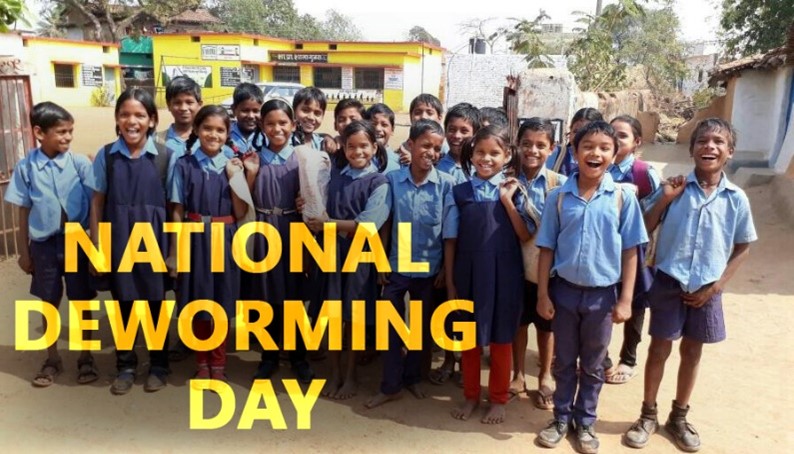
Our Work
Ongoing Projects
Past Projects
Our Clients and Partners





This is the heading
Do you know the Elementor image box height? Offering the best image box wordpress plugin.

This is the heading
Offering the Elementor image box with button. We are offering image box carousel elementor

This is the heading
Do you know how to add image box in WordPress website with elementary. Download Elementskit.